Les personnes abonnées au service Amazon Prime, bénéficient de plusieurs services en plus de la réception de colis en 1 jour ouvre.
Nous allons exploiter une faille dans le service Amazon Photo qui est compris dans l’abonnement Amazon Prime.
Pour bénéficier du stockage photo en illimité, il faut uploader des images au format jpeg. Tous les autres fichiers seront facturé.
Si on prend une image au format jpeg, qu’on append à la fin du fichier un deuxième fichier (peut importe le type ou la taille) et qu’on upload le fichier sur Amazon photo, l’upload s’éffectue et lors du download, le fichier téléchargé sera identique au fichier uploadé :D.
Il reste plus qu’à extraire le fichier caché dans la photo.
Notre photo en hexa avec un fichier et l’offset ou ce trouve le fichier pour pouvoir l’extraire.
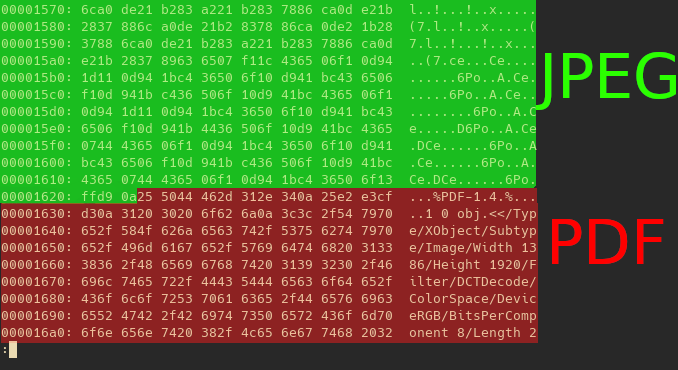
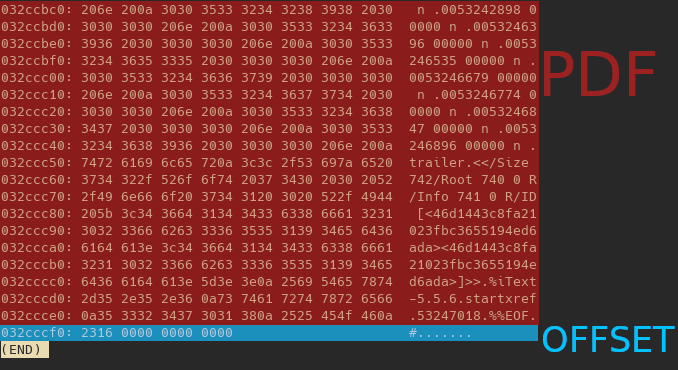
Notre fichier contient toujours l’image
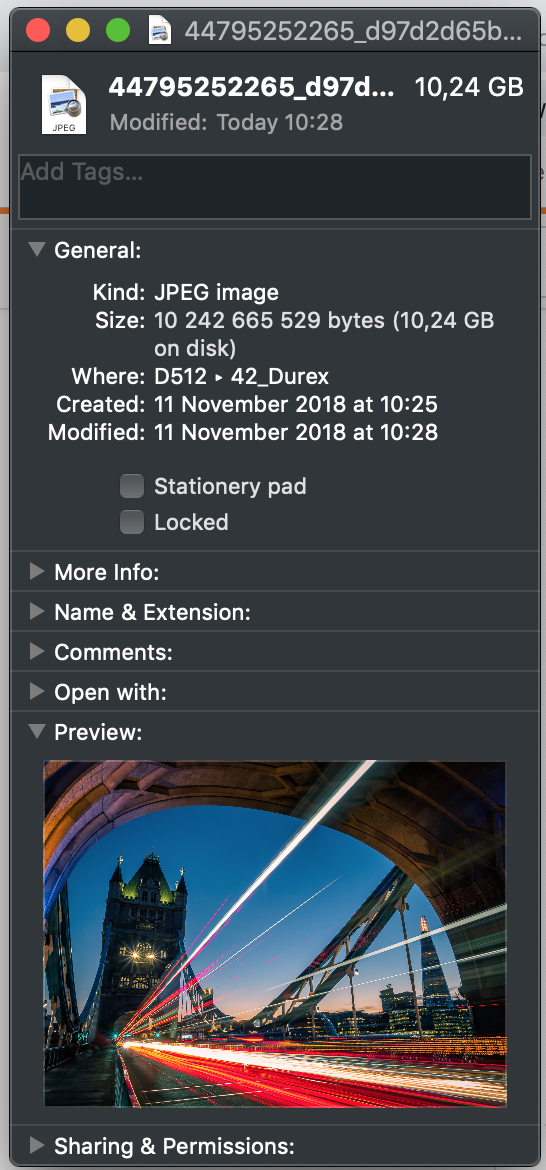
le fichier original et le fichier telechargé sont toujours identiques
❯ shasum *
ae8c0f1f07c5cf1f40e346dcb1532c411a7a7dd5 44795252265_d97d2d65b8_o.jpg
ae8c0f1f07c5cf1f40e346dcb1532c411a7a7dd5 44795252265_d97d2d65b8_o_amazon.jpg
Et le fichier ce trouve bien dans le stockage dedié à amazon photo
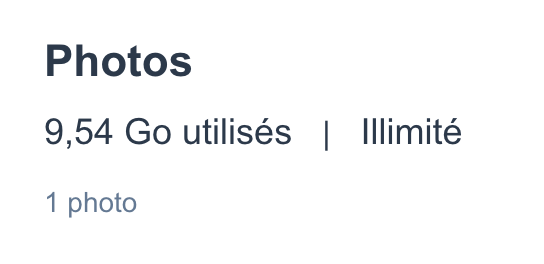
Il y à une limite d’upload. Un fichier ne peut pas depasser 50 Go.
Testé avec une image de 1x1 pixel, ca fonctionne aussi :D.
Clique -> Le code pour cacher un fichier dans une image :
// To compile this code : gcc append.c -o append
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
static inline bool usage(int argc)
{
if (argc != 3) {
puts("Usage : ./fusion photo.jpeg file_append");
return (false);
}
return (true);
}
int open_files(char **argv, int *fd_source, int *fd_target)
{
if ( (*fd_source = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_APPEND)) == -1) {
perror("open");
return (errno);
}
if ( (*fd_target = open(argv[2], O_RDONLY)) == -1) {
perror("open");
return (errno);
}
return (0);
}
off_t go_to_end_of_file(int fd_source)
{
off_t offset = 0;
offset = lseek(fd_source, 0, SEEK_END);
if (offset == -1) {
perror("lseek");
return (-1);/
}
return (offset);
}
bool write_to_file(int fd_source, int fd_target)
{
int ret = 0;
char *buff = NULL;
// Alloc buffer for read;
buff = calloc(sizeof(char), 4096);
if (buff == NULL) {
printf("calloc error");
return (false);
}
// read target file in jpeg file
while ((ret = read(fd_target, buff, (size_t)4096)) > 0)
write(fd_source, buff, (size_t)ret);
free(buff);
buff = NULL;
if (ret == -1) {
perror("write");
return (false);
}
return (true);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd_source = 0;
int fd_target = 0;
off_t offset = 0;
// Print usage if command bad formatted
if (usage(argc) == false)
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
// Open source file and target file
open_files(argv, &fd_source, &fd_target);
// move file offset at end
offset = go_to_end_of_file(fd_source);
if (offset == -1)
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
// append target file in source file
if (write_to_file(fd_source, fd_target) == false)
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
// write offset where our target begin at end of file
write(fd_source, &offset, sizeof(offset));
close(fd_source);
close(fd_target);
puts("Fusion success");
}
Clique -> Le code pour recuperer notre fichier :
// To compile this code : gcc split.c -o split
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
static inline bool usage(int argc, char *bin)
{
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage : %s file_to_split new_file", bin);
return (false);
}
return (true);
}
static off_t get_offset(int fd)
{
off_t size_file = 0;
struct stat st;
fstat(fd, &st);
// set offset where the size is stored
if (lseek(fd, (off_t)st.st_size - (off_t)sizeof(size_file), SEEK_SET) == -1) {
perror("lseek");
exit(errno);
}
// read size of hidden file
if (read(fd, &size_file, sizeof(size_file)) < 1) {
perror("read");
exit(errno);
}
// replace offset at begin
if (lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET) == -1) {
perror("lseek");
exit(errno);
}
return (size_file);
}
static bool split(int fd, off_t offset, char *file)
{
struct stat st;
char *buff = NULL;
int ret = 0;
int fd_new_file = 0;
fstat(fd, &st);
lseek(fd, offset, SEEK_SET);
buff = calloc(sizeof(char), 4096);
if (buff == NULL) {
printf("calloc error");
return (false);
}
// Create new file
if ((fd_new_file = open(file, O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0744)) == -1) {
perror("open");
free(buff);
buff = NULL;
exit (errno);
}
// write hiddent file in new file
while ((ret = read(fd, buff, (size_t)4096)) == 4096)
write(fd_new_file, buff, (size_t)ret);
// write last part without offset
if ((unsigned long)ret > sizeof(off_t))
write(fd_new_file, buff, (size_t)ret - sizeof(off_t));
free(buff);
buff = NULL;
return (true);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd = 0;
off_t offset = 0;
// Print usage if command bad formatted
if (usage(argc, argv[0]) == false)
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
}
offset = get_offset(fd);
if (split(fd, offset, argv[2]) == false)
return (EXIT_FAILURE);
printf("%s created !", argv[2]);
return (0);
}